Tiny Function Generator Sine Wave
7th March 2018
This article describes an update to my Tiny Function Generator program to add a sine wave to the existing seven waveforms it provides:
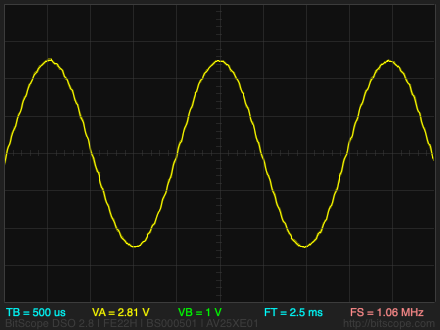
The Tiny Function Generator has been one of my most popular projects, but several people made the valid comment that it was a pity that it didn't include a sine wave. I realised that this could be added quite simply by providing an array of 256 points, defining one cycle of a sine function.
I could have precalculated the values and included them as constants in the program. However, it seemed more interesting to calculate them in the program.
I have designed a PCB for this circuit: see Tiny Function Generator PCB.
The program
The program works by first calculating the sine waveform in a 256-byte array, and this is then used by the DDS to generate the sine wave output.
The waveform is stored in the array Sinewave[]:
int8_t Sinewave[256];
Here's the routine CalculateSine() to calculate one cycle of a sine wave:
void CalculateSine () {
int X=0, Y=8180;
for (int i=0; i<256; i++) {
X = X + (Y*4)/163;
Y = Y - (X*4)/163;
Sinewave[i] = X>>6;
}
}
The for loop uses the Minsky circle algorithm to calculate the 256 points in a sine wave, without needing floating point or trig functions. The value 4/163 is a close approximation to (2*π)/256, where 2*π is the number of radians in a circle, ie one cycle, and 256 is the number of subdivisions of the circle we want.
An additional Sine() routine then outputs the points from the Timer/Counter0 COMPA interrupt when you select the sine wave:
void Sine () {
Acc = Acc + Jump;
OCR1A = Sinewave[Acc>>8] + 128;
}
The "+ 128" converts the signed 8-bit values in the Sinewave[] array to an unsigned 8-bit number for the OCR1A counter.
There's also a new icon to represent the sine wave.
Other details
The circuit and other details are unchanged from the previous project; see Tiny Function Generator.
Here's the updated program: Tiny Function Generator Sine Wave program.
blog comments powered by Disqus
